
As a result, both the UK and International Accounting Standards provide accountants with more information in order to retained earnings clarify the situation. Receive the latest financial reporting and accounting updates with our newsletters and more delivered to your inbox. Using Q&As and examples, KPMG provides interpretive guidance on research and development costs and funding arrangements. The arrangements may be designed to shift licensing rights, intellectual property ownership, an equity stake, or a share in the profits to the sponsors.


A piece of software is considered technologically feasible when you’ve determined it’s possible to create the product and can reasonably assume it will provide value to customers in the future. Your documentation system should capture several key elements that support your accounting practices. While ERIS offers a higher payable rate (up to ~27%) for qualifying loss-making SMEs, its accounting treatment remains identical to the merged scheme. GAAP and IFRS, and provides clear examples of expense recognition and capitalization. Zero-based budgeting, which involves building budgets from the ground up and justifying each expense, promotes efficient resource allocation and minimizes waste. Scenario analysis is another valuable tool, allowing companies to evaluate the potential impact of market conditions, technological advancements, or regulatory changes on R&D efforts.
Some companies will outsource their R&D because they lack the resources to conduct it internally, depending on others to promote innovation. Some companies have departments entirely devoted to Research and Development, while others decide to contract out their R&D. Pharmaceutical companies often use allocation methods to assign indirect costs to various projects.

The Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 174 allows deduction of R&D expenses, but the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act mandates amortizing these costs over five years for tax years starting after December 31, 2021. This shift demands careful planning to optimize tax strategies while maintaining compliance. This conservative approach ensures companies maintain accurate and consistent reporting, capturing the true nature of R&D as an uncertain yet essential investment in future growth.
Supplemental disclosures describing the activities and objectives of R&D programs also builds understanding of how those costs translate to future products, revenue growth, and improved margins. Overall though, capitalizing R&D better accounts https://www.bookstime.com/ for these vital investments companies make in long-term growth and competitiveness. The costs are now aligned with the innovations and intellectual property generated. Existing deferred tax assets for stock-based compensation may be impacted as compensation for covered employees may no longer be deductible due to the change in aggregation rules. Companies will need to assess whether these deferred tax assets should be written off upon enactment.
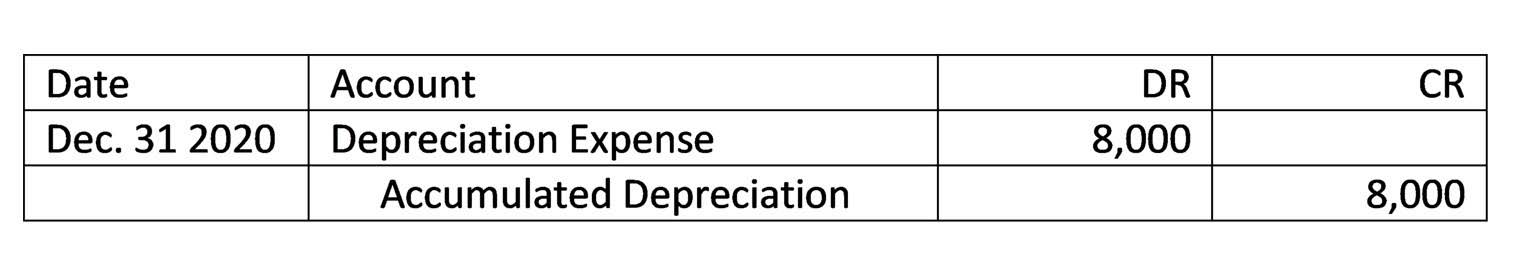
Enhanced disclosures around significant judgments and assumptions also promotes transparency. In any case, following accounting standards what is r&d in accounting helps provide consistency and comparability for financial statement users. Trends in R&D spending can indicate rising or falling investments in innovation for a company relative to competitors. While the new standards aim to improve financial reporting, they also introduce complexities around determining useful lives and impairment of capitalized R&D. Companies will need robust processes to estimate amortization periods and track asset performance.